Profibus
Posted on 21 August, 2022
What is PROFIBUS?
A PROFIBUS system uses a bus master to poll slave devices distributed model on an RS485 serial bus. A ProfiBus slave is any peripheral device (I/O transducer, valve, network drive, or other measuring device) which processes information and sends its output to the master.
PROFIBUS communication is half duplex, which means that only 1 device is communicating at a time. One thing to note while creating a PROFIBUS network is that it can become a fault sensitive network.
General brief on its cabling and connectors
PROFIBUS uses 7/9 pins in the D-sub connectors with pin 2 and 7 not in use. Or in most purposes, mainly the pin 3,5,6, and 8. Pin 3 & 8 are used for data transmission (which is where you connect the green (+) and red (-) wire) And pin 5 & 6 for termination.
& oh, don't forget the loop resistance of the standard Profibus DP cable is 110 Ω/km. (Side note: Be aware that a standard Profibus PA cable has a loop resistance of 44 Ω/km.) This can be achieved by inserting a 220 Ω resistor in each end of the Profibus line.
As there tend to be potential differences between stations during installation, the connection of the shield is crucial to avoid noise. Infact, no current should run in our shielding, so do remember to ground your stations appropriately to ground!
Advancement of PROFIBUS
To deep dive a little deeper, there's many different protocol of Profibus as well, as such, Profibus DP (Decentralised Periphery) and Profibus-PA (Process Automation). ProfiBus DP normally operates using a cyclic transfer of data between master(s) and slave(s) on an RS485 network. And Profibus-PA is a variant of Profibus DP that is specially designed for improvement and replacement of conventional systems such as 4-20 mA and HART in process automation.
But fret not, actually there is nearly not much difference between them! So what exactly sets them apart? It's baud-rate and transporation of data and power supply. PROFIBUS DP can transport 244 bytes of data from 9600 bit/s up to 12 Mbit/s, while PROFIBUS-PA runs at a fixed transmission speed of 31250 bit/s. Why? The speed of the PROFIBUS is relative to the length of your cable.
The RS485 balanced transmission used in PROFIBUS DP only allows 31 devices to be connected at once; however, more devices (upto 126) can be connected or the network expanded with the use of hubs or repeaters (4 hubs or repeaters to reach 126). A Hub or a Repeater is also counted as a device. In contrast to PROFIBUS DP, data and power supply are transported over the same two wires and there is an explosion proof option available.
Thus, this enables a more efficient network structure, making it even more economical. As most PLC has a PROFIBUS DP connection, we need a segment coupler to convert PROFIBUS-PA signals to PROFIBUS DP signals. Here is a diagram to help you visualise better~
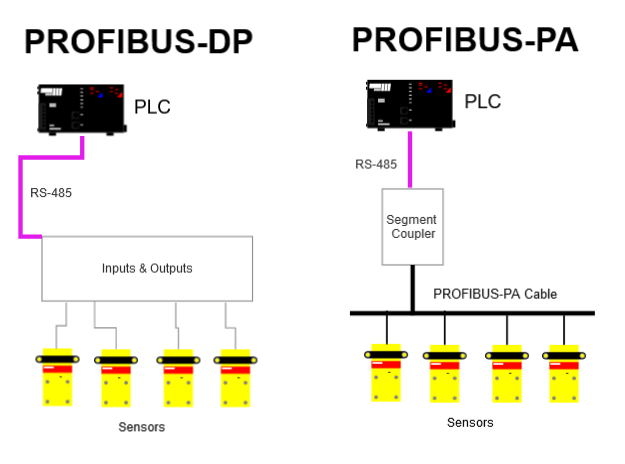
Due to its high speed capabilities, PROFIBUS DP is mostly used for factory automation and PROFIBUS PA is mostly used in industries such as water treatment, oil, gas, chemical, explosives, etc.
Some other common terminology you can deep dive into if you would like to understand more about the PROFIBUS technology and protocol would include:
Class 1 Master –
- Central controller that exchanges I/O data with connected slaves.
- Determines the baud rate (slaves auto-detect this rate).
- Manages the token transfer between masters. Detects another master during the gap time.
Class 2 Master –
- Diagnostic, configuration, or startup tool.
- Can only control one slave at a time.
- Does not have write-access to the slave.
- Does not have a GSD file.
Slave -
- A passive station which can only respond per a master request and acknowledge messages. A slave has no bus control rights.
- The GSD file defines the slave for the master.